- Home
- /
- Services
Heat Pump
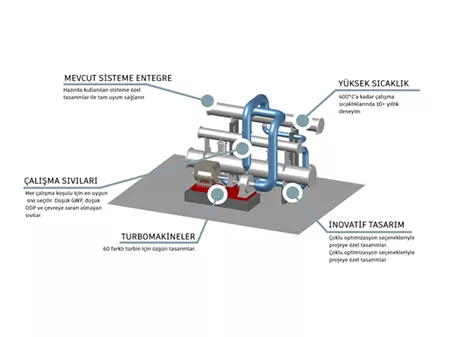
Heat Pump
Industrial Heat Pump:
Revolutionizing Manufacturing Processes Heat pumps are succeeding in this field by using renewable energy sources and utilizing thermodynamic principles. By extracting thermal energy from the environment (such as air, water or soil), heat pumps can provide high levels of heat in various manufacturing processes with low energy input. This efficiency, in addition to providing significant cost savings, makes heat pumps an attractive investment for manufacturers looking to optimize their operating processes.
Cost Savings and Operating Efficiency:
Heat pump applications offer manufacturers the opportunity to reduce energy costs and increase operating efficiency. By replacing traditional heating and cooling systems with heat pumps, businesses can benefit from lower energy bills due to reduced energy consumption. Additionally, heat pumps require minimal maintenance, which helps reduce downtime such as repairs and downtime. With improved efficiency and cost effectiveness, manufacturers can direct business resources to other important areas of their operations.
Environmental Responsibility:
Manufacturers have a responsibility to minimize their environmental impact. Heat pumps fit this goal perfectly, using renewable energy sources and operating without producing direct emissions. By using heat pumps, manufacturers can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a cleaner, greener future. This commitment to sustainability also enhances the company's brand image and reputation, attracting environmentally conscious customers and business partners.
Various Application Areas:
Heat pumps offer a variety of applications at different stages of the production process. From heating and cooling in industrial processes to waste heat recovery, heat pumps can be customized to a variety of needs. This versatility allows manufacturers to optimize energy use in various areas of their operations, increasing overall efficiency and productivity.
Government Incentives and Compliance:
Governments around the world are promoting energy efficiency and sustainability initiatives. As a manufacturer adopting heat pump technology, you can receive various incentives, grants and tax deductions provided by government bodies. These incentives not only reduce the initial investment cost but also facilitate compliance with environmental regulations. By taking advantage of these programs, manufacturers can achieve rapid transition to sustainable practices as well as financial benefits.
Application examples:
1. Process Heating and Cooling: Heat pumps can efficiently provide heating or cooling for a variety of manufacturing processes. Whether it is maintaining optimal temperatures in chemical reactions, material heat treatment or climate control in production facilities, heat pumps offer precise and reliable temperature control, increasing process efficiency and product quality.
2. Space Heating and Cooling: Heat pumps are an excellent solution for heating and cooling large manufacturing spaces such as warehouses, factories and assembly areas. By using renewable energy sources, heat pumps can effectively maintain comfortable indoor temperatures while reducing energy consumption and operating costs.
3. Hot Water Production: Heat pumps can be used for efficient hot water production in manufacturing facilities. For disinfection processes, cleaning operations or running facilities, heat pumps can provide a constant and reliable supply of hot water while significantly reducing energy consumption compared to traditional water heating systems.
4. Waste Heat Recovery: Manufacturing processes often generate significant amounts of waste heat. Heat pumps can capture this waste heat and convert it into usable thermal energy for other indoor heating applications. By using waste heat recovery systems, manufacturers can increase overall energy efficiency, reduce energy costs and minimize environmental impact.
5. HVAC Systems: Heat pumps can be integrated into HVAC (Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning) systems that combine heating and cooling capabilities. These systems provide energy-efficient climate control for offices, laboratories, clean rooms and other manufacturing areas. They reduce energy consumption and operating costs while providing a comfortable working environment for employees.
6. Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Systems: Heat pumps can be combined with power generation systems such as gas turbines or piston engines to create Combined Heat and Power (CHP) systems. These systems simultaneously generate electricity and use waste heat for heating or other thermal processes, maximizing energy efficiency and reducing dependence on external energy sources.
Join Our Newsletter
Be informed about innovations about us



