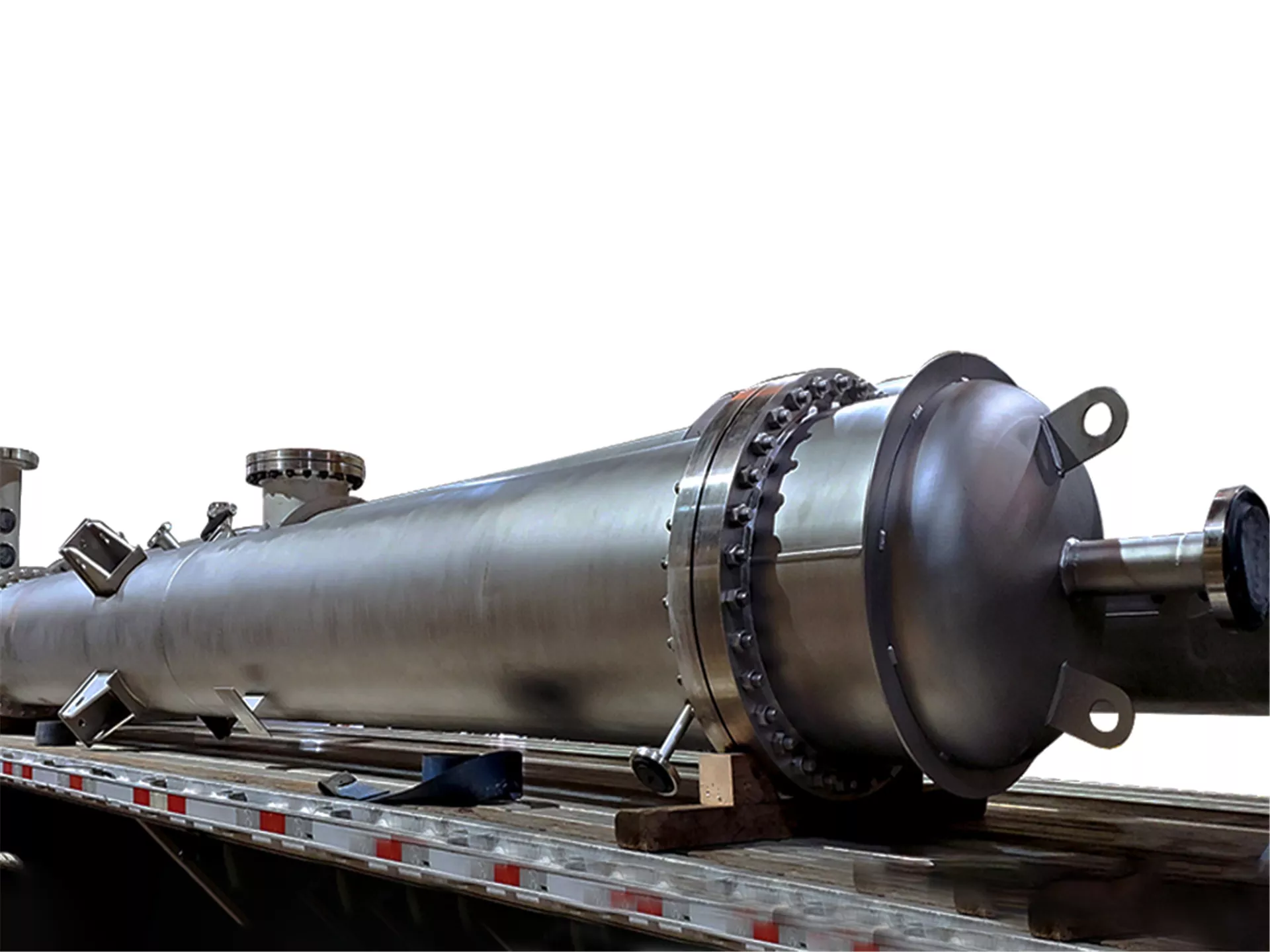
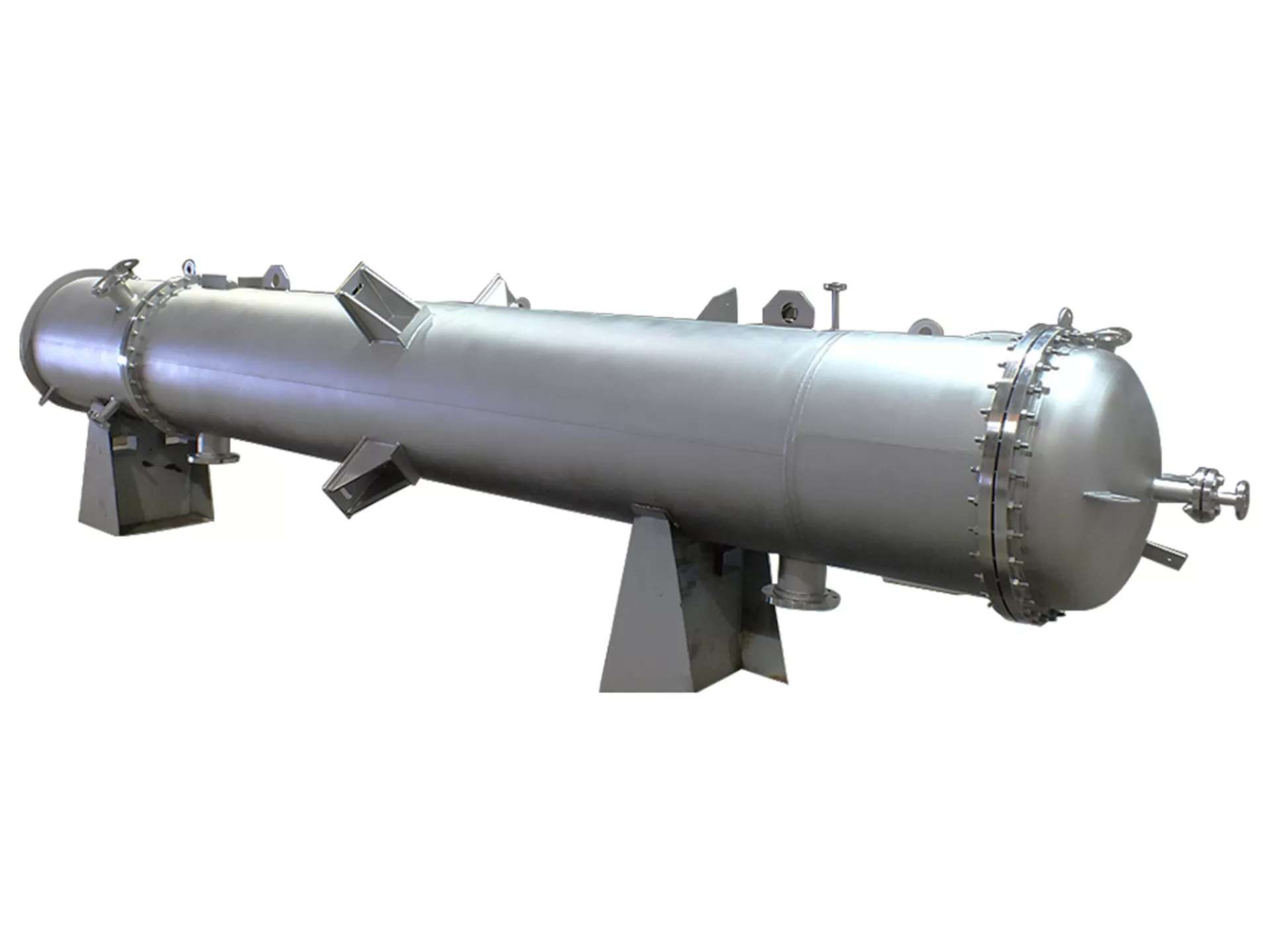
Name of the Product You Will Order: Heat Exchanger
Heat Exchanger

Heat Exchanger
Heat exchangers are innovative equipment that enables heat transfer between two or more fluids. By leveraging thermal engineering principles, exchangers have become a critical tool in improving energy efficiency, reducing costs and promoting sustainable practices across a variety of industries.
Improved Productivity with Efficient Heat Transfer
Heat exchangers form the basis of many industrial processes by helping to transfer thermal energy efficiently. During processes such as heating, cooling or heat recovery, these equipment enable manufacturers to maximize productivity while minimizing energy consumption.
When heat is produced in production processes, exchangers capture this excess energy and make it reusable. This excess heat can be transferred to other parts of the system or different production processes, resulting in significant energy savings. This not only reduces operating costs but also helps reduce the overall environmental impact of production activities.
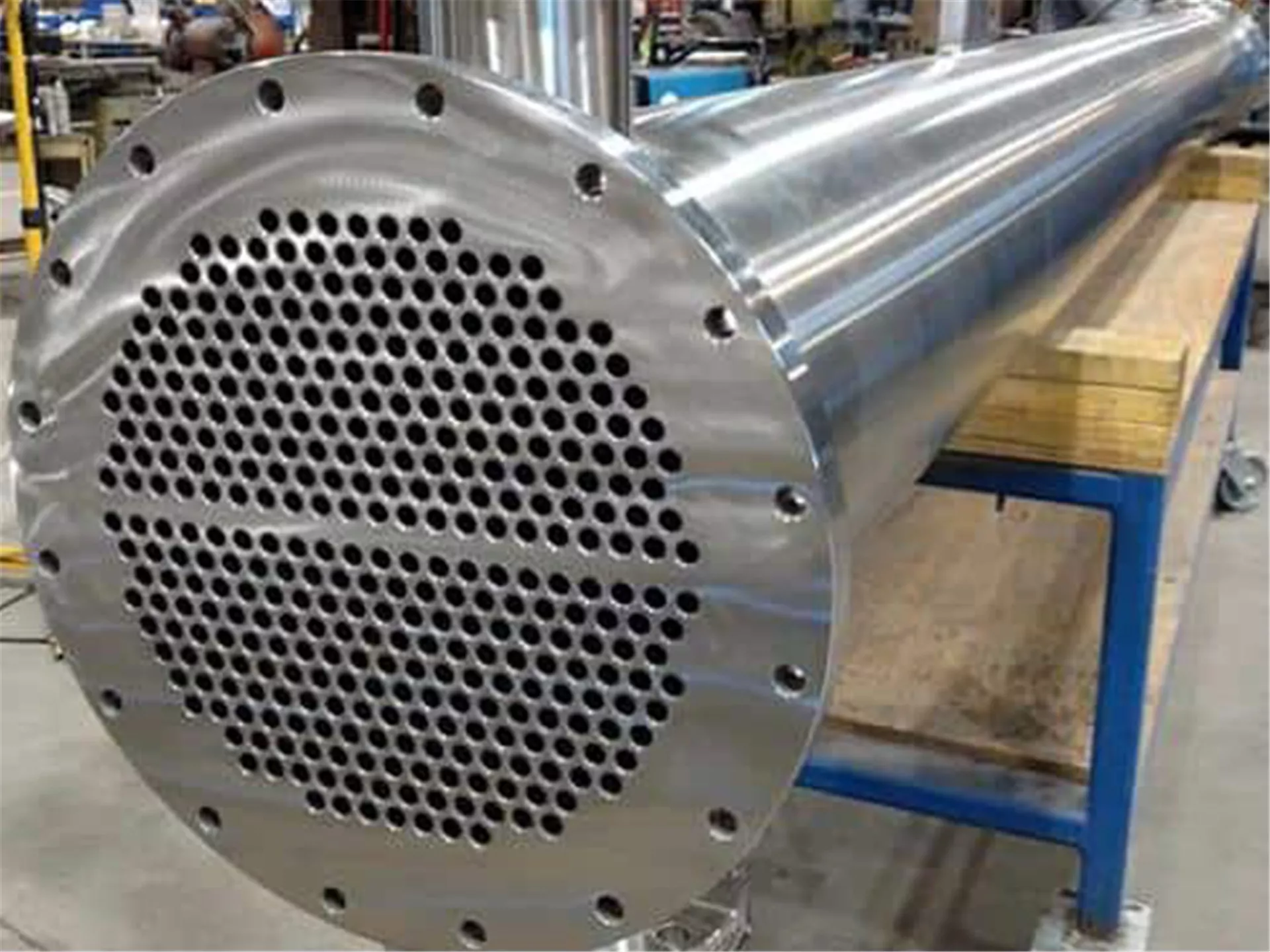
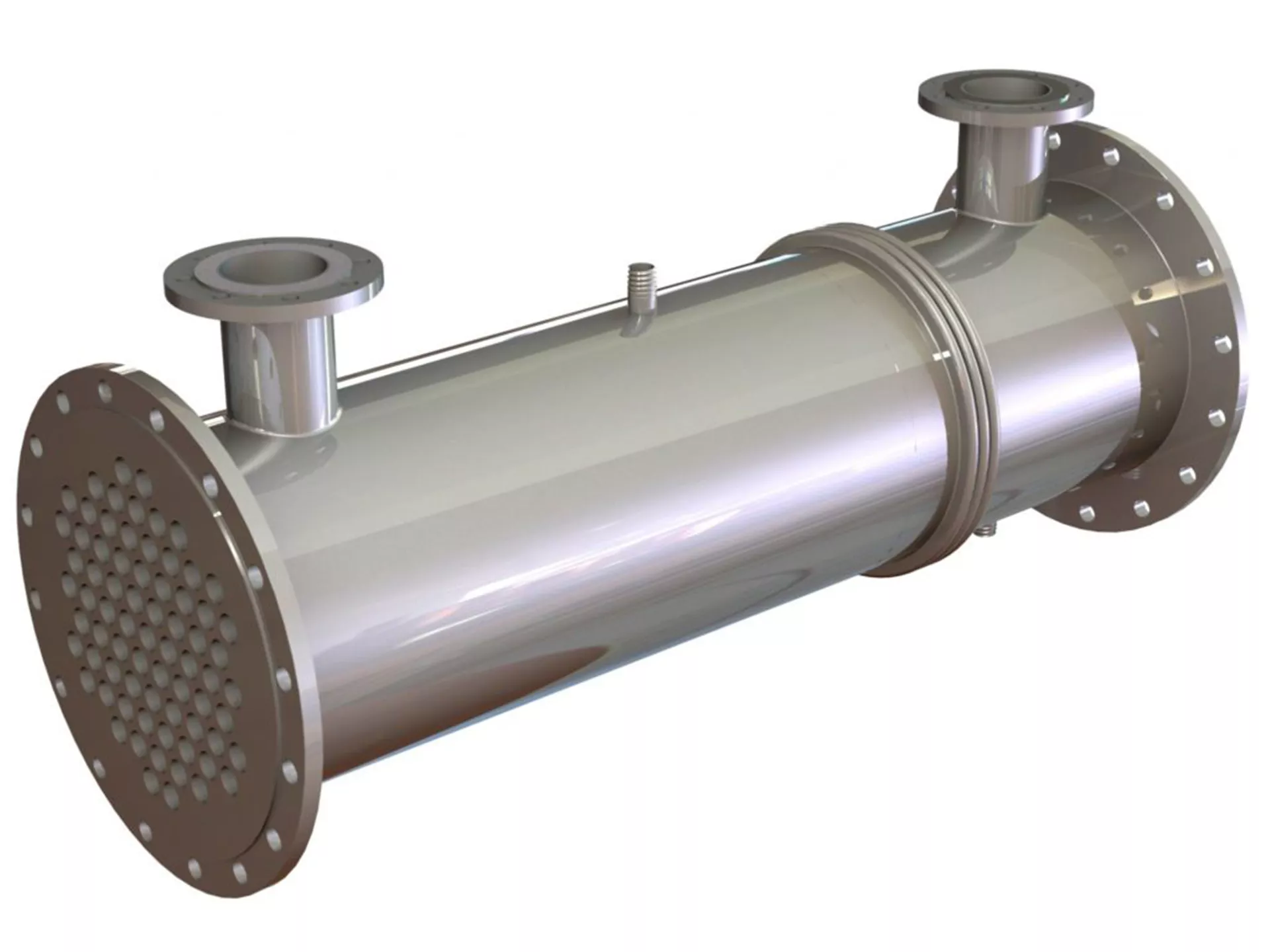
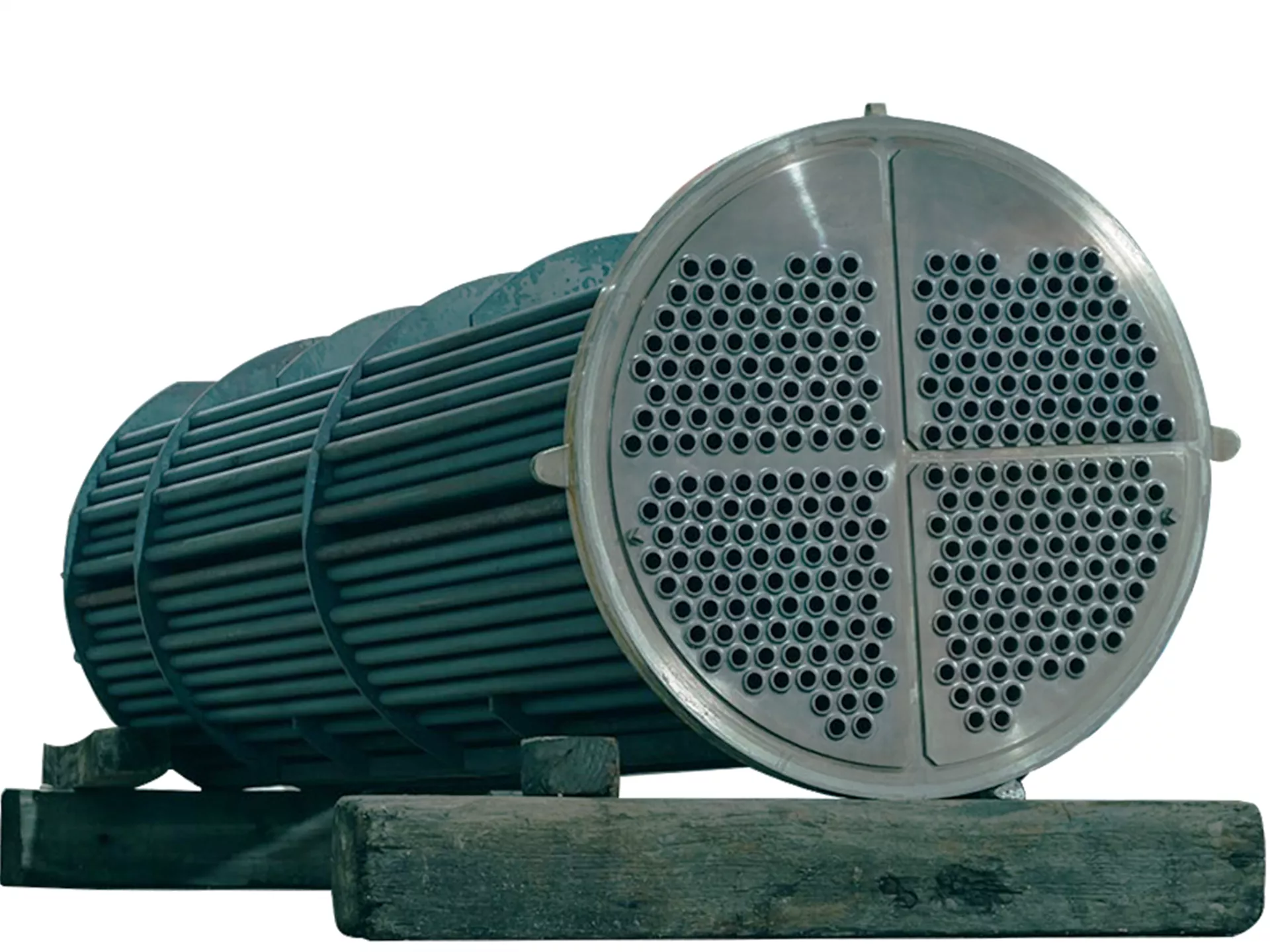
Tubular Heat Exchanger: Efficient and Versatile
One of the most commonly used heat exchanger types in industry is the tube heat exchanger. These exchangers consist of a bundle of tubes placed inside a shell. During heat transfer, a transfer occurs between a fluid flowing through the tubes (fluid on the tube side) and another fluid flowing inside the shell, outside the tube bundle (fluid on the shell side).
The fluid passing through the pipe is generally the fluid that needs heating or cooling, while the fluid on the shell side receives or gives off the necessary heat. This design provides a large surface area and low pressure drop for effective heat transfer.
Some advantages of tube heat exchangers are:
High Heat Transfer Efficiency: The design of tubular exchangers offers a large surface area to ensure efficient heat transfer between two fluids. This means effective temperature control and better process performance.
Versatility: Shell and tube heat exchangers can adapt to a variety of applications in low to high pressure and low to high temperature ranges. They can handle a variety of fluids such as liquids, gases and even two-phase mixtures, so they are extremely versatile in a variety of industries.
Scalability and Flexibility: These switchers can be customized and scaled according to specific production needs. Properties such as the number and size of pipes and the configuration of fluid paths within the shell can be adjusted to optimize heat transfer efficiency.
Finned-tube exchangers: Maximizing Heat Transfer Surface Area
Another type of heat exchanger commonly used in production processes is finned tube heat exchangers. These exchangers consist of fins added to the outer surface of the pipe. Fins increase heat exchange efficiency by significantly increasing the heat transfer surface area.
Some advantages of finned tube heat exchangers are:
Increased Heat Transfer Surface Area: Fins added to the outer surface of the pipe improve heat transfer by creating a larger surface area. This provides more effective heat exchange, better temperature control and energy savings.
Improved Heat Transfer Rate: Fins disrupt the boundary layer of the fluid, promoting turbulence and providing better heat transfer rates. This enables effective heat transfer even with fluids with low thermal conductivity.
Compact Design: Finned tube heat exchangers have a high heat transfer surface area to volume ratio, making them suitable for space-limited applications. Their compact design enables easy installation and integration into existing systems.
Heat exchangers such as tube and finned tube exchangers are indispensable tools for manufacturers to optimize energy efficiency, reduce costs and promote sustainable production. These versatile equipment offer the advantage of increasing energy efficiency, reducing costs, improving product quality and ensuring environmental sustainability by providing effective heat capture and distribution. With the advancement of technology, greater efficiency gains in heat exchanger designs and a brighter future for sustainable production are expected.
Aluminum Tube Heat Exchanger
When choosing the right heat exchanger for industrial applications, manufacturers often face the challenge of choosing between aluminum and steel tube heat exchangers. Both materials have their unique advantages, but in recent years aluminum heat exchangers have gained significant popularity due to their outstanding properties and performance. In this article, we will discuss the advantages of aluminum tube heat exchangers over steel ones to help manufacturers make an informed decision.
Lightweight and Corrosion Resistant:
One of the important advantages of aluminum tube heat exchangers is their lightness. Aluminum is a significantly lighter metal than steel. This feature makes aluminum heat exchangers easier to handle, transport and install in a variety of industrial environments. Additionally, aluminum has excellent corrosion-resistant properties. It forms a natural oxide layer and is thus protected from environmental factors such as moisture and chemicals, ensuring long-term durability and minimizing maintenance requirements.
Superior Heat Transfer Efficiency:
Aluminum is known for its exceptional thermal conductivity, meaning a superior heat transfer efficiency. Compared to steel, aluminum has a higher heat transfer coefficient, allowing for an efficient and rapid heat exchange between the two fluids. This feature leads to improved overall performance, reduced energy consumption and increased efficiency in production processes.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings:
Thanks to their high heat transfer efficiency, aluminum tube heat exchangers can achieve the desired temperature change with less energy input. This energy efficiency contributes to environmental sustainability by reducing carbon emissions while reducing operational costs. By choosing aluminum exchangers, manufacturers can benefit from significant energy savings and achieve long-term cost advantages.
Flexibility and Customization:
Aluminum tube heat exchangers offer excellent flexibility and customization options. Aluminum is a highly malleable material, allowing complex designs and configurations to be realized according to specific process requirements. Manufacturers can easily tailor heat exchanger design to optimize tube layout and surface area for their unique application. This flexibility allows the exchanger to precisely meet the needs of the production process, thus achieving optimal performance and efficiency.
Non-Magnetic and Non-Arcing Features:
Unlike steel, aluminum is non-magnetic and does not arc, making it suitable for applications where these properties are important. Industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing and electronics require non-magnetic and non-arcing equipment to ensure safety and prevent accidents. Aluminum tube heat exchangers provide a reliable solution in these industries by eliminating the risk of magnetic interference and sparks.
As a result, Aluminum tube heat exchangers offer many advantages such as lightweight structure, corrosion resistance, superior heat transfer efficiency, energy saving, flexibility and non-magnetic/arcing. These benefits help manufacturers improve their operations, increase energy efficiency and achieve long-term cost savings. By choosing aluminum heat exchangers, manufacturers can optimize their processes, reduce maintenance requirements and contribute to a sustainable production environment.